Question: Seedlings use seed storage proteins as
an important nitrogen source during germination. The seed …
Seedlings use seed storage proteins as
an important nitrogen source during germination. The seed storage
proteins are made as large precursors, then hydrolyzed to smaller
products for the seedling’s use during growth. In this case, the
investigators discovered a new seed storage protein, which they
named BN, in the oilseed
Brassica nigra. These seeds are important nutritionally as a
source of oil as well as protein. The storage protein described
here was first purified and then characterized for its important
biochemical properties. The storage protein turned out to be an
inhibitor of serine protease enzymes. The authors hypothesized that
the purpose of serine protease inhibitors like BN is to protect the
plant from proteolytic enzymes of insects and microorganisms that
would damage the plant. The protein BN likely belongs to a
family of seed storage proteins
called napins, which typically consist of two non-identical
disulfide-bonded polypeptide chains. Napins make up as much as 20%
of the protein content of seeds.
In
order to isolate the protein, seeds were ground and extracted with
water. The proteins in the extract were precipitated with
hydrochloric acid and the pellet isolated by centrifugation was
discarded. The supernatant was heated to 70°C to remove heat-labile
proteins, then lyophilized (freeze-dried). The lyophilized powder
was dissolved in a small amount of ammonium acetate buffer at pH =
5 and the sample was loaded onto a Sephadex G-251 gel filtration
column. The elution profile showed four peaks. Most of the BN
protein eluted in the first peak.
a. On what basis is separation achieved
on the Sephadex gel filtration column?
b. Compare the BN protein size to other
proteins found in the B. nigra seeds.
Following gel filtration
chromatography, the BN protein was further purified by dialysis
using tubing with a 6000-
8000 molecular weight cut-off. Analysis
using SDS-PAGE (in the absence of ?-mercaptoethanol) showed a
single band. The results are shown in Figure 7.1.
c. Why is the BN protein more pure
after the dialysis step?
d. Why was the gel run in the absence
of ?-mercaptoethanol?
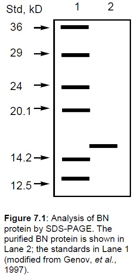
Show transcribed image text Std, kD 2 24 14.2 12.5 Figure 7.1: Analysis of BN protein by SDS-PAGE. The purified BN protein is shown in Lane 2; the standards in Lane 1 modified from Genov, et al. 1997
Std, kD 2 24 14.2 12.5 Figure 7.1: Analysis of BN protein by SDS-PAGE. The purified BN protein is shown in Lane 2; the standards in Lane 1 modified from Genov, et al. 1997



