Question: Cdc13 forms separate complexes with different functions at
telomeres. Cell cycle regulated post-t…
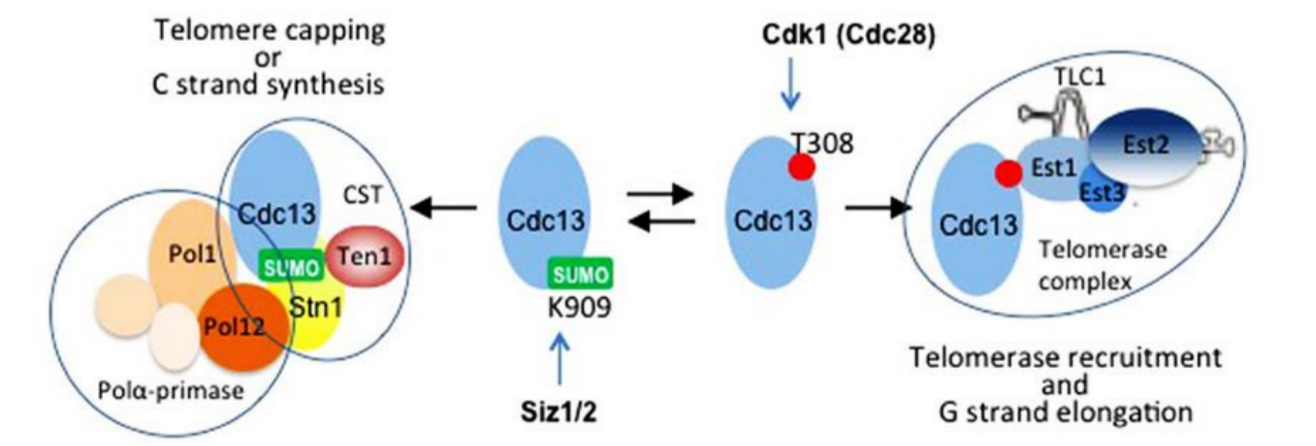
Cdc13 forms separate complexes with different functions at
telomeres. Cell cycle regulated post-translational modifications of
cdc13 control the balance between these complexes. The current
model is presented in the figure below.
SUMOylation is a type of post-translational modification (PTM)
on proteins. Siz1- and/or Siz2-dependent SUMOylation on Lys909
located in the C-terminus of Cdc13 promotes its interaction with
Stn1 and formation of the CST complex. This modification peaks in
early to mid S-phase.
Cyclin-dependent kinase Cdk1 phosphorylates cdc13 on Thr308.
This residue is critical for the recruitment of telomerase by
cdc13. This modification occurs in late S to G2- phases, and it
favors the interaction of Cdc13 with Est1 at the expense of its
interaction with Stn1, thus promoting telomere uncapping and
telomerase recruitment .
When telomerase action is accomplished, Cdc13 switches back to
interaction with Stn1, and CST complex recruits pol?-primase for
the C-strand synthesis. Other modifications are likely involved in
fine-tuning the balance between the complexes formed by Cdc13.
Explain fully how either sumoylation or phosphorylation PTM can
modify the types the interactions in which cdc13 is engaged.
Show transcribed image text Telomere capping or C strand synthesis Cdk1 (Cdc28) TLC1 308 Est1 Est3 dc13 Cdc13 Cdc13 Cdc13 Telomerase complex Pol1 Ten1 SUMO SUMO K909 Stn1 Pol1 Telomerase recruitment and G strand elongation Pola-primase Siz1/2
Telomere capping or C strand synthesis Cdk1 (Cdc28) TLC1 308 Est1 Est3 dc13 Cdc13 Cdc13 Cdc13 Telomerase complex Pol1 Ten1 SUMO SUMO K909 Stn1 Pol1 Telomerase recruitment and G strand elongation Pola-primase Siz1/2



