A 55-year-old man is admitted to the emergency department aftera motor vehicle accident. The patient is hemorrhaging from alacerated spleen and requires emergency surgery. Pretransfusiontesting determines that the patient’s phenotype is group A,D-negative type with a negative antibody screen. Crossmatches withred blood cell units are compatible by the immediate-spincrossmatch. During surgery, the patient receives 6 units of groupA, D-negative red blood cells and 4 units of group A frozen plasma.Three days later, during the first 15 minutes of a subsequent redblood cell transfusion using a blood-warming device, the patientdevelops fever and chills.
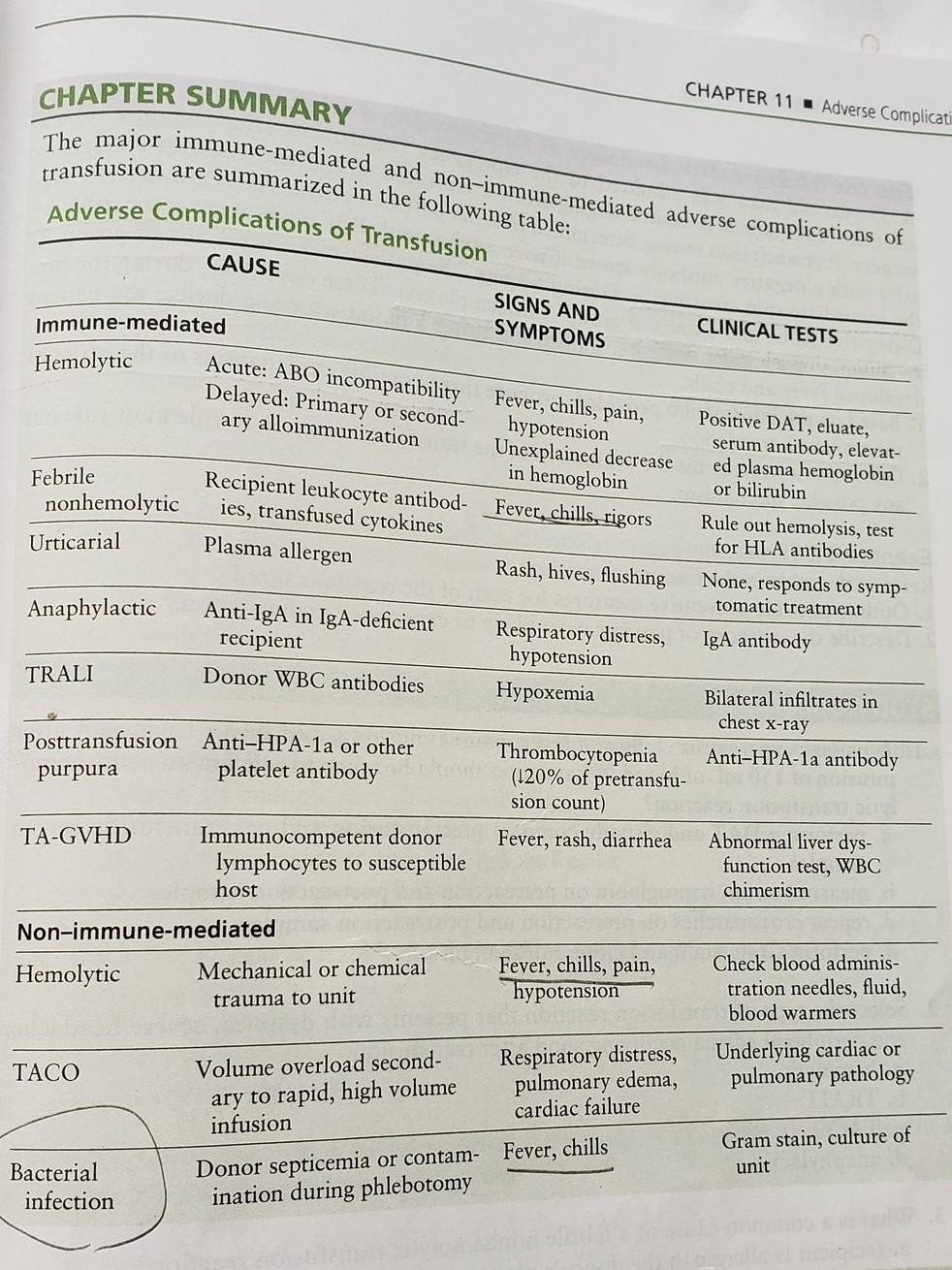
Refer to the table in the chapter Summary.
1.Outline possible preventive measures for each of the reactionslisted.
2. Describe the category of patients most likely to experienceeach reaction.