
Transcribed Image Text from this Question
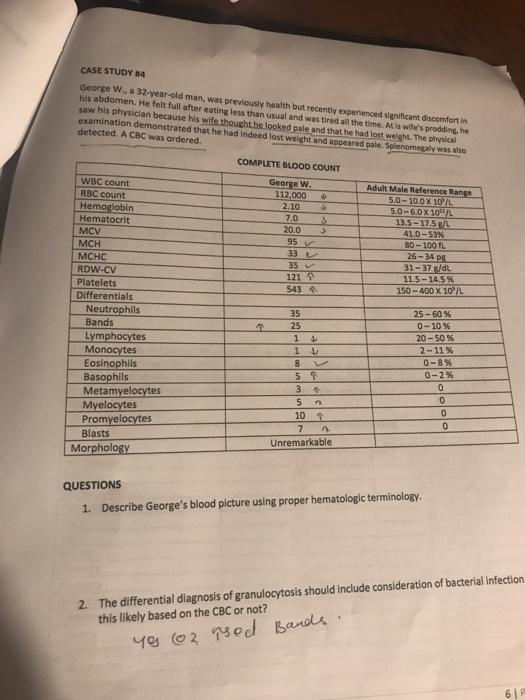
CASE STUDY 34 George W., a 32-year-old man, was previously health but recently experienced significant discomfortin his abdomen. He felt full after eating less than usual and was tired all the time. Atis wife’s predding, he saw his physician because his wife thought he looked pale and that he had lost weigM. The physical examination demonstrated that he had indeed lost weight and appeared pale. Splenomegaly was also detected. A CBC was ordered. COMPLETE BLOOD COUNT WBC count George W. Adult Male Reference Range RBC count 112,000 5.0 – 100X10/L 2.10 Hemoglobin 5.0-6.0X10 Hematocrit 7.0 13.5-1758L 20.0 MCV 41.0 -53% 95 80 – 100 TL MCH 33 26 -34 DE MCHC 35 31-37/dL RDW-CV 115-14.5% Platelets 543 150 – 400 X 10°/L Differentials Neutrophils 35 25-60% Bands 25 0-10% Lymphocytes 1 20-50% Monocytes 1 L 2-11% 8 0-8% Eosinophils 5 0-2% Basophils 3 Metamyelocytes 0 5 Myelocytes 10 1 Promyelocytes 7 Blasts Unremarkable Morphology 121 이이이이 QUESTIONS 1. Describe George’s blood picture using proper hematologic terminology. 2. The differential diagnosis of granulocytosis should include consideration of bacterial infection this likely based on the CBC or not? yos (02 rood Bands 3. Considering the CBC findings and George’s age, what condition is most likely 4. The promyelocytes and blasts outnumber the myelocytes and metamyelocytes. What is this called? 5. What additional testing is needed, and what results would confirm Wayne’s diagnosis? Why?
(Visited 5 times, 1 visits today)



