Question: Consider a population of frogs. Allele B_1 codes for spotted frogs; allele B_2 codes for non-spot…
how gene flow (migration) affects allele frequencies in island
populations
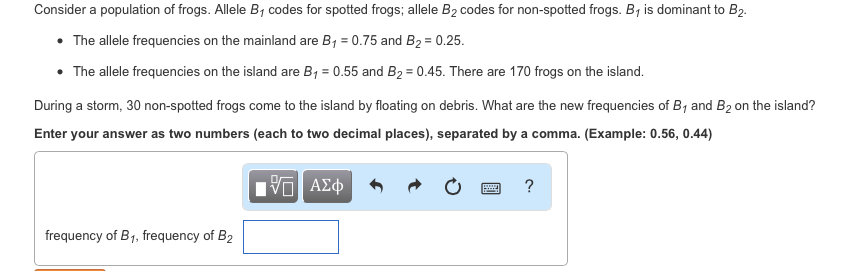
Show transcribed image text Consider a population of frogs. Allele B_1 codes for spotted frogs; allele B_2 codes for non-spotted frogs. B_1 is dominant to B_2 The allele frequencies on the mainland are B_1 = 0.75 and B_2 = 0.25. The allele frequencies on the island are B_1 = 0.55 and B_2 = 0.45. There are 170 frogs on the island. frequency of B_1, frequency of B_2 During a storm, 30 non-spotted frogs come to the island by floating on debris. What are the new frequencies of B_1 and B_2 on the island? Enter your answer as two numbers (each to two decimal places), separated by a comma.
Consider a population of frogs. Allele B_1 codes for spotted frogs; allele B_2 codes for non-spotted frogs. B_1 is dominant to B_2 The allele frequencies on the mainland are B_1 = 0.75 and B_2 = 0.25. The allele frequencies on the island are B_1 = 0.55 and B_2 = 0.45. There are 170 frogs on the island. frequency of B_1, frequency of B_2 During a storm, 30 non-spotted frogs come to the island by floating on debris. What are the new frequencies of B_1 and B_2 on the island? Enter your answer as two numbers (each to two decimal places), separated by a comma.



