Question: Consider the Wnt signal transduction pathway in the figure. The
Wnt signal
transduction pathway i…
Consider the Wnt signal transduction pathway in the figure. The
Wnt signal
transduction pathway is important in the development of intestinal
cells, and in
intestinal cancers. Assume that transcription of the target gene(s)
promotes cell
division.
 a.
a.
Identify two proteins in the Wnt pathway, the genes for which you
predict could
be oncogenes (proto-oncogenes). Justify or explain your answer for
each.
b. Identify two proteins in the Wnt pathway, the genes for which
you predict could
be tumor suppressor genes. Justify or explain your answer for
each.
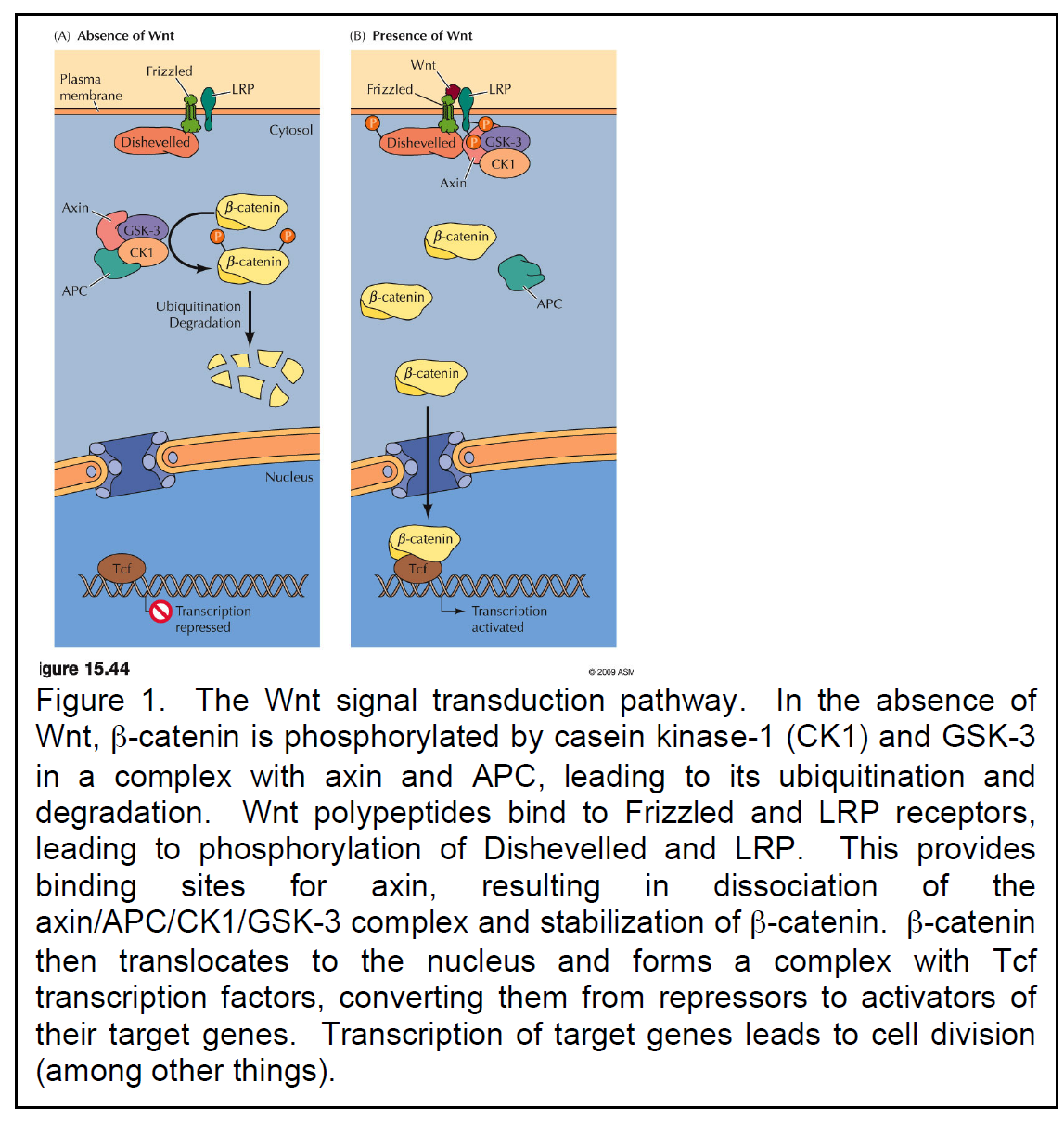
Show transcribed image text (A) Absence of Wnt (B) Presence of Wnt Wnt Frizzled Plasma LRP Frizzled LRP mémbrane Cytosol Dishevelled Dishevelled CP GSK-3 CK1 Axin Axin β-catenin β-catenin CK1 β-catenin APC β-catenin APC Ubiquitination Degradation β-catenin Nucleus β-catenin Tcf Transcription repressed Transcription activated gure 15.44 2009 ASI Figure 1. The Wnt signal transduction pathway. In the absence of Wnt, β-catenin is phosphorylated by casein kinase-1 (CK1) and GSK-3 in a complex with axin and APC, leading to its ubiquitination and degradation. Wnt polypeptides bind to Frizzled and LRP receptors, leading to phosphorylation of Dishevelled and LRP. This provides binding sites for axin, resulting in dissociation of the axin/APC/CKI/GSK-3 complex and stabilization of β-catenin. β-catenin then translocates to the nucleus and forms a complex with Tcf transcription factors, converting them from repressors to activators of their target genes. Transcription of target genes leads to cell division (among other things)
(A) Absence of Wnt (B) Presence of Wnt Wnt Frizzled Plasma LRP Frizzled LRP mémbrane Cytosol Dishevelled Dishevelled CP GSK-3 CK1 Axin Axin β-catenin β-catenin CK1 β-catenin APC β-catenin APC Ubiquitination Degradation β-catenin Nucleus β-catenin Tcf Transcription repressed Transcription activated gure 15.44 2009 ASI Figure 1. The Wnt signal transduction pathway. In the absence of Wnt, β-catenin is phosphorylated by casein kinase-1 (CK1) and GSK-3 in a complex with axin and APC, leading to its ubiquitination and degradation. Wnt polypeptides bind to Frizzled and LRP receptors, leading to phosphorylation of Dishevelled and LRP. This provides binding sites for axin, resulting in dissociation of the axin/APC/CKI/GSK-3 complex and stabilization of β-catenin. β-catenin then translocates to the nucleus and forms a complex with Tcf transcription factors, converting them from repressors to activators of their target genes. Transcription of target genes leads to cell division (among other things)



