Question: In this module the role of actin in hippocampal neurons will be investigated. The hippocampus is …
Part 1 multiple choice

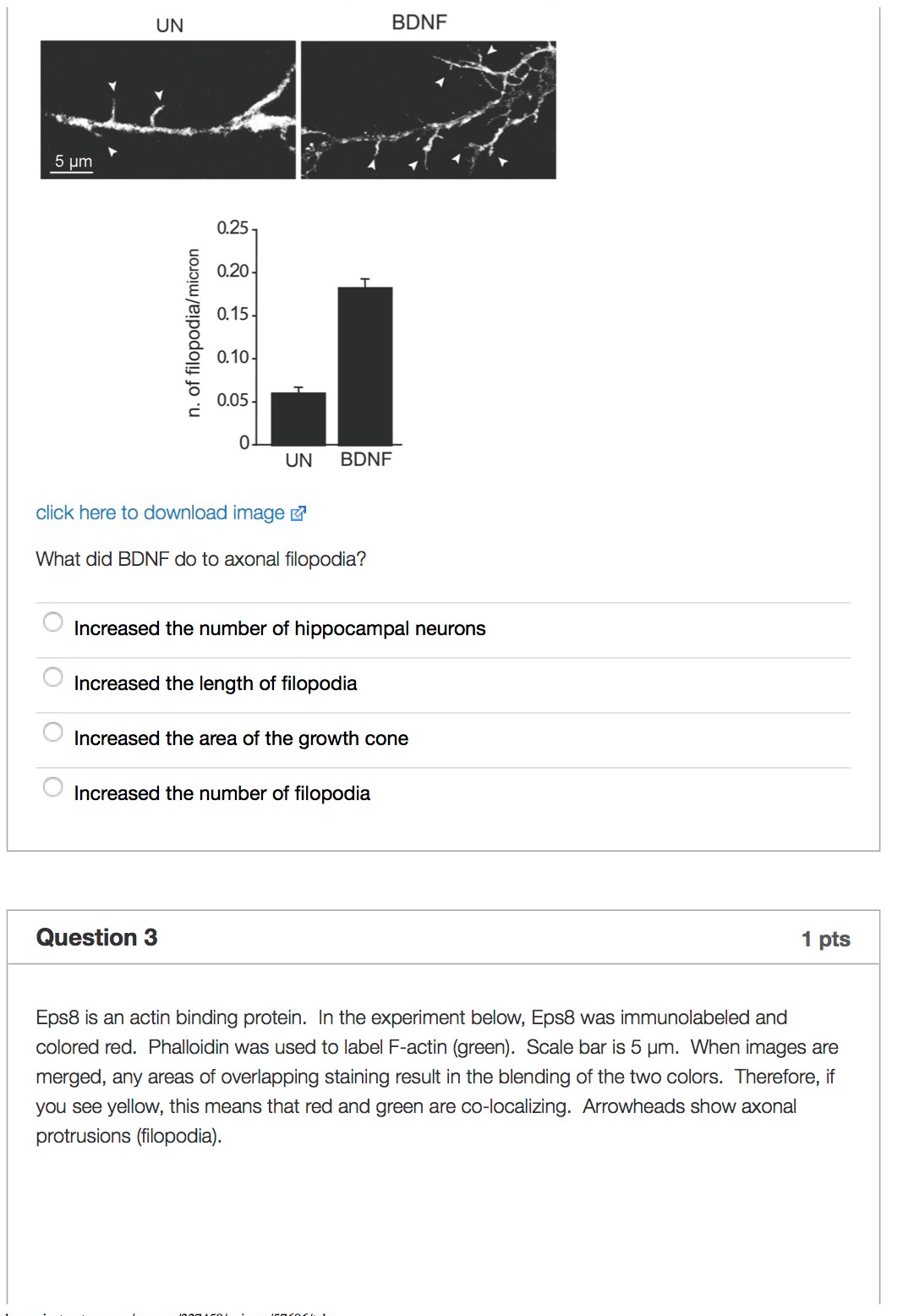

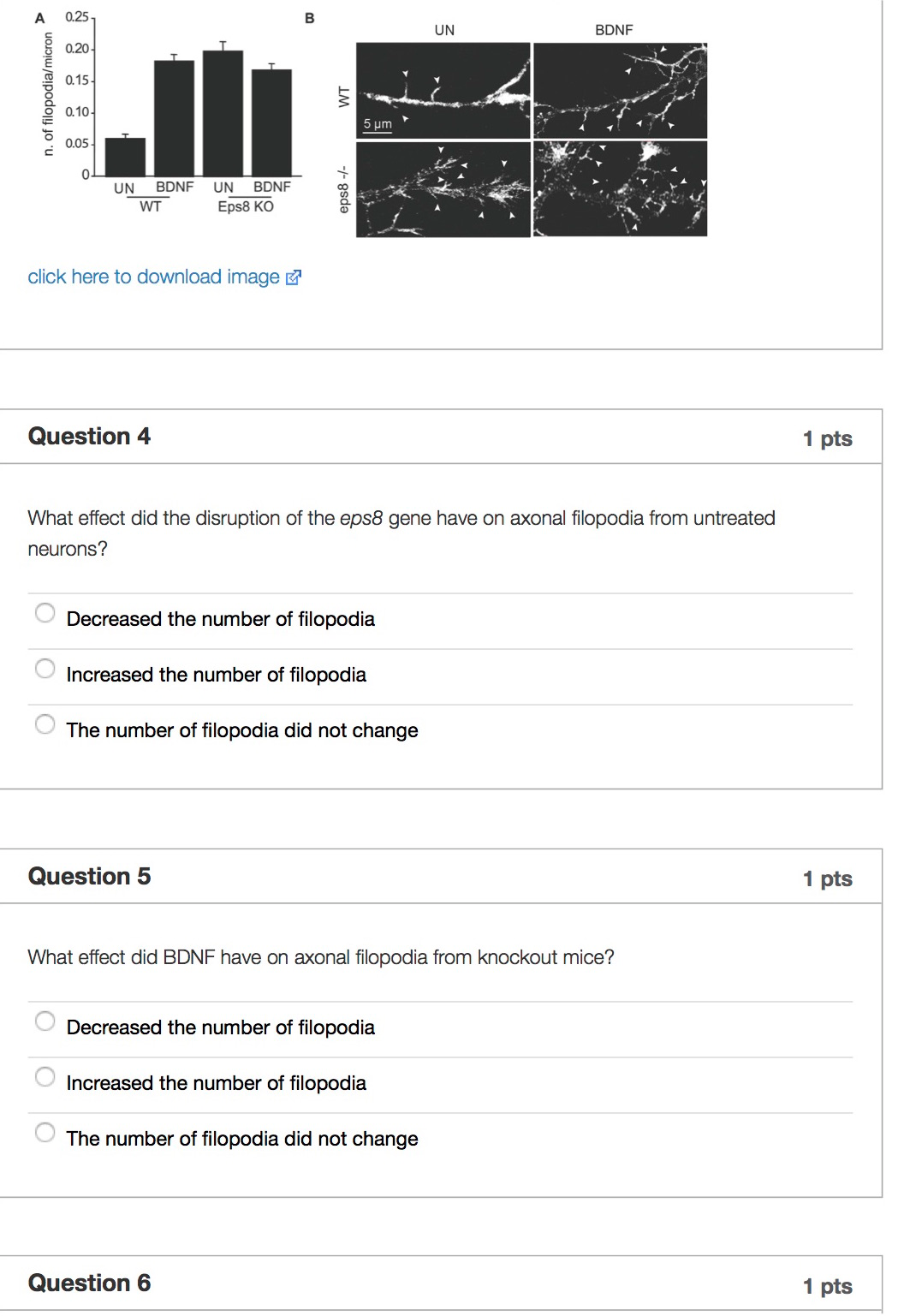


Show transcribed image text In this module the role of actin in hippocampal neurons will be investigated. The hippocampus is a key brain region that processes experiences and decides whether to assign that experience to long term memory. Memories and learning require the formation of new connections between neurons called synapses. Also, during development, neurons need to make new connections/synapses with other neurons. We already investigated the growth cone in the last module. In this module, we will investigate the filopodia that are produced along the axon. Question 1 1 pts From your general biology knowledge, what are filopodia? Static, thin, finger-like protrusions of actin. Dynamic, flat, broad, sheet-like protrusions of actin. Dynamic, thin, finger-like protrusions of actin. Static, thin, finger-like protrusions of microtubules that are powered and bend back and forth. Question 2 1 pts Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) binds to and activates Trk, a tyrosine kinase receptor. BDNF controls growth and differentiation of the brain during development. In the experiment below, hippocampal neurons from 3 day old mouse pups were cultured in vitro. Some were treated with BDNF, the others remained untreated (UN). Cells were fixed and fluorescently stained for F-actin. Scale bar is 5 μm. The number of filopodia (arrowheads) from many cells was counted and expressed per micron of axon length
In this module the role of actin in hippocampal neurons will be investigated. The hippocampus is a key brain region that processes experiences and decides whether to assign that experience to long term memory. Memories and learning require the formation of new connections between neurons called synapses. Also, during development, neurons need to make new connections/synapses with other neurons. We already investigated the growth cone in the last module. In this module, we will investigate the filopodia that are produced along the axon. Question 1 1 pts From your general biology knowledge, what are filopodia? Static, thin, finger-like protrusions of actin. Dynamic, flat, broad, sheet-like protrusions of actin. Dynamic, thin, finger-like protrusions of actin. Static, thin, finger-like protrusions of microtubules that are powered and bend back and forth. Question 2 1 pts Brain derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) binds to and activates Trk, a tyrosine kinase receptor. BDNF controls growth and differentiation of the brain during development. In the experiment below, hippocampal neurons from 3 day old mouse pups were cultured in vitro. Some were treated with BDNF, the others remained untreated (UN). Cells were fixed and fluorescently stained for F-actin. Scale bar is 5 μm. The number of filopodia (arrowheads) from many cells was counted and expressed per micron of axon length



