Transcribed Image Text from this Question
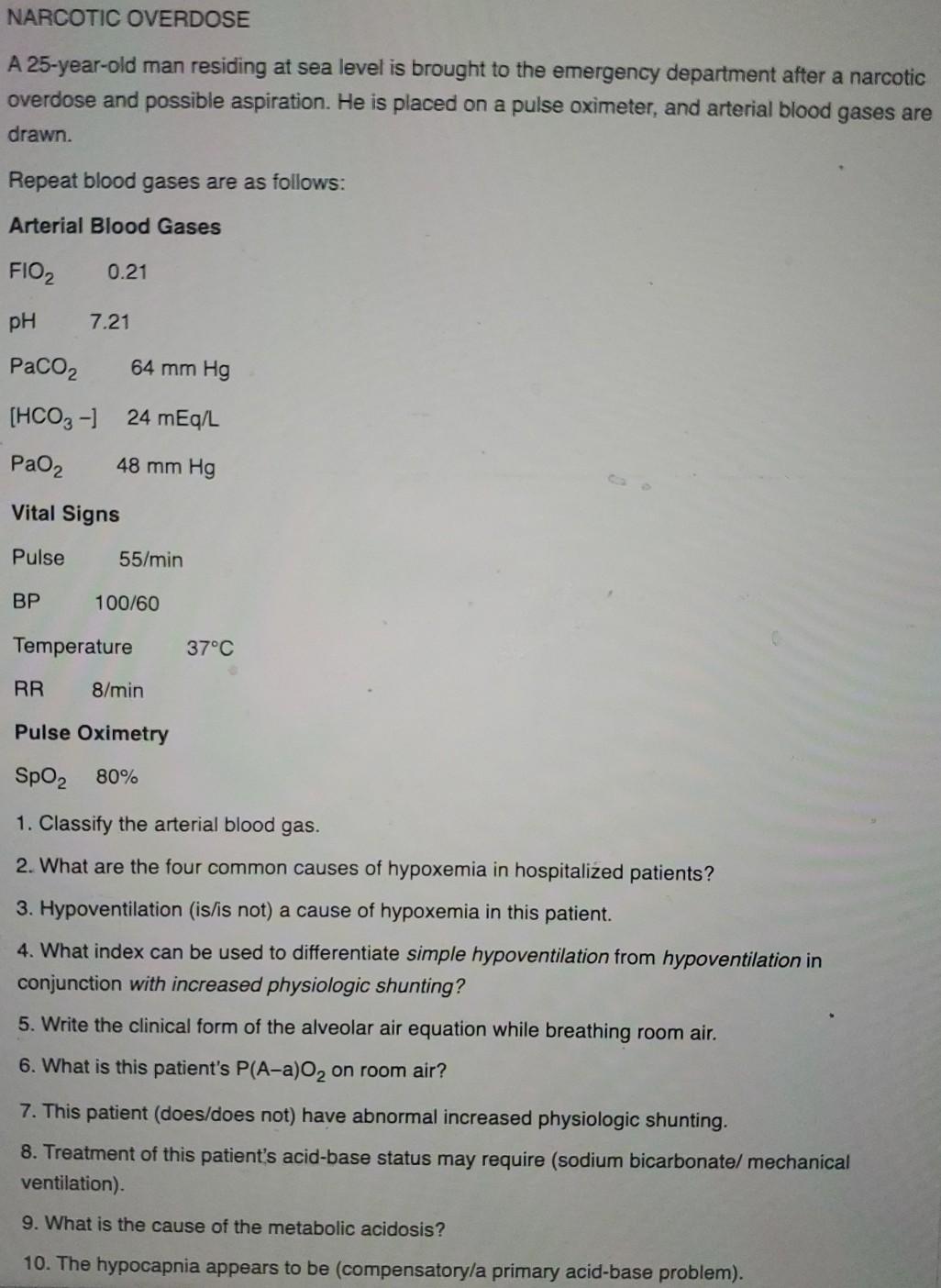
NARCOTIC OVERDOSE A 25-year-old man residing at sea level is brought to the emergency department after a narcotic overdose and possible aspiration. He is placed on a pulse oximeter, and arterial blood gases are drawn. Repeat blood gases are as follows: Arterial Blood Gases FIO2 0.21 pH 7.21 PaCo2 64 mm Hg (HCO3-) 24 mEq/L Paoz 48 mm Hg Vital Signs Pulse 55/min BP 100/60 Temperature 37°C RR 8/min Pulse Oximetry SpO2 80% 1. Classify the arterial blood gas. 2. What are the four common causes of hypoxemia in hospitalized patients? 3. Hypoventilation (is/is not) a cause of hypoxemia in this patient. 4. What index can be used to differentiate simple hypoventilation from hypoventilation in conjunction with increased physiologic shunting? 5. Write the clinical form of the alveolar air equation while breathing room air. 6. What is this patient’s P(A-a)02 on room air? 7. This patient (does/does not) have abnormal increased physiologic shunting. 8. Treatment of this patient’s acid-base status may require (sodium bicarbonate/ mechanical ventilation). 9. What is the cause of the metabolic acidosis? 10. The hypocapnia appears to be compensatory/a primary acid-base problem).
(Visited 5 times, 1 visits today)