Question: Protein Tyrosine Phosphataso-1B in Diabetes Pathway (practice PSA cont.) PTP1B is localized to th…
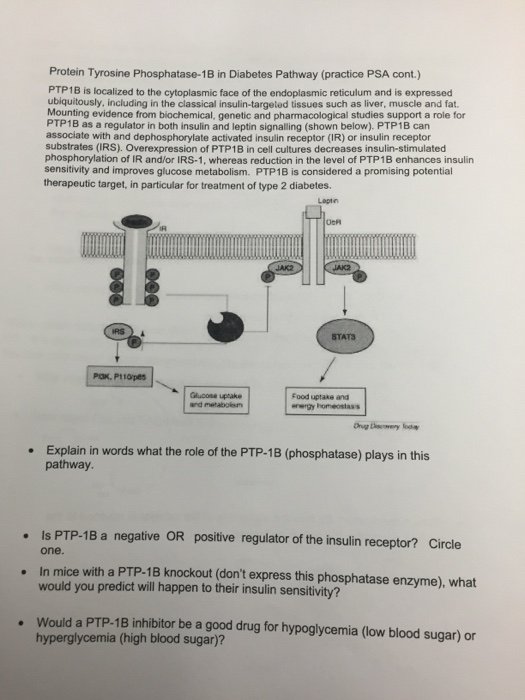
Show transcribed image text Protein Tyrosine Phosphataso-1B in Diabetes Pathway (practice PSA cont.) PTP1B is localized to the cytoplasmic face of tho endoplasmic reticulum and is expressed ubiquitously, including in the classical insulin-targeted tissues such as liver, muscle and fat. Mounting evidence from biochemical, genetic and pharmacological studies support a role for PTP1B as a regulator in both insulin and leptin signalling (shown below). PTP1B can associate with and dephosphorylate activated insulin receptor (IR) or insulin receptor substrates (IRS). Overexpression of PTP1B in cell cultures decreases insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of IR and/or IRS-1, whereas reduction in the level of PTP1B enhances insulin sensitivity and improves glucose metabolism. PTP1B is considered a promising potential therapeutic target, in particular for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Explain in words what the role of the PTP-1B (phosphatase) plays in this pathway. Is PTP-1B a negative OR positive regulator of the insulin receptor? Circle one. In mice with a PTP-1B knockout (don't express this phosphatase enzyme) what would you predict will happen to their insulin sensitivity? Would a PTP-1B inhibitor be a good drug for hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar)?
Protein Tyrosine Phosphataso-1B in Diabetes Pathway (practice PSA cont.) PTP1B is localized to the cytoplasmic face of tho endoplasmic reticulum and is expressed ubiquitously, including in the classical insulin-targeted tissues such as liver, muscle and fat. Mounting evidence from biochemical, genetic and pharmacological studies support a role for PTP1B as a regulator in both insulin and leptin signalling (shown below). PTP1B can associate with and dephosphorylate activated insulin receptor (IR) or insulin receptor substrates (IRS). Overexpression of PTP1B in cell cultures decreases insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of IR and/or IRS-1, whereas reduction in the level of PTP1B enhances insulin sensitivity and improves glucose metabolism. PTP1B is considered a promising potential therapeutic target, in particular for treatment of type 2 diabetes. Explain in words what the role of the PTP-1B (phosphatase) plays in this pathway. Is PTP-1B a negative OR positive regulator of the insulin receptor? Circle one. In mice with a PTP-1B knockout (don't express this phosphatase enzyme) what would you predict will happen to their insulin sensitivity? Would a PTP-1B inhibitor be a good drug for hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) or hyperglycemia (high blood sugar)?



