Transcribed Image Text from this Question
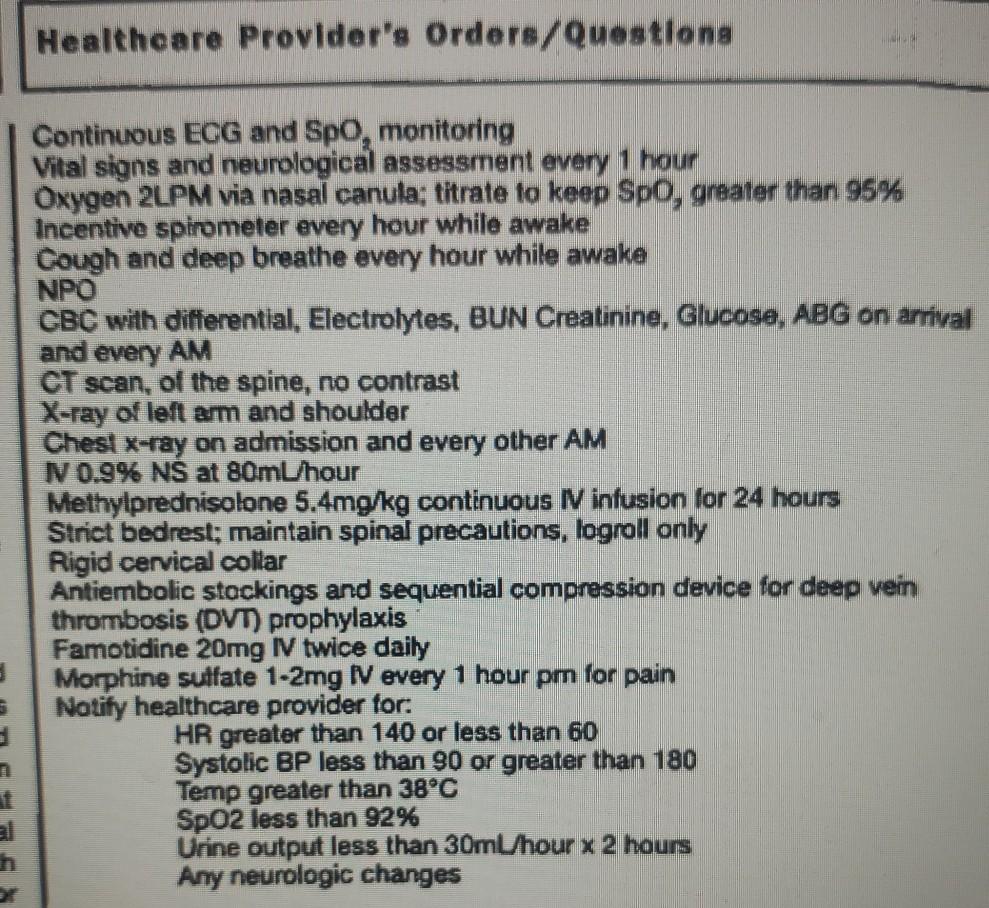
Simulated Clinical Experience (SCET) Overview Scenario File Name: Neurogenic Shock Overlay on: Standard Man Location: Neurological Intensive Care Unit Synopsis: This simulated clinical experience presents the leamer with a young adult male patient who fell 30 feet from the roof of the house he was building. At the scene, the young man complained he could not feel or move either of his legs. The young man was transported via emergency medical services to a local Emergency Department and was evaluated and transferred to the regional spinal cord Injury (SCI) center. On arrival to the SCI center, the young man was directly admitted to the Neurological Intensive Care Unit (ICU). The learner will have the opportunity to experience basic ICU admission procedures and treatments. During this simulated clinical experience, the learner encounters the various stages of neurogenic shock and the expected treatments and outcomes. There are five states that are transitioned manually, including an optional arterial line insertions state. This simulated clinical experience is intended for leamers in Semester IV. History/Information: The patient, a 20-year-old male, was a crew member on a construction team building a house when he slipped and tripped on building materials and fell 30 feet from the roof. The patient hit the ground with a thud, and his co-workers went running to his aid and called emergency medical services (EMS). The patient was moaning and conversing with one of his buddies who continuously reminded him to be still and not to try to move. EMS arrived on the scene and found the patient alert and oriented and immediately stabilized his neck with a rigid cervical collar. At the scene, the patient stated he could not feel or move either of his legs and his left hand felt numb and tingly. Initial history and physical at the scene found the patient was a normal, healthy young adult male with no previous health history, respiratory rate and effort adequate, pulses palpable and strong in all four extremities, skin warm and color normal with brisk capillary refill, left arm painful to slight touch and gross motor movement adequate (able to wiggle fingers). Noted forearm deformity with associated pain without movement. Paresthesia extended from between the nipple line and umbilicus with no movement noted in bilateral lower extremities. His initial vital signs at the scene were reported to be HR 92, BP 128/86, RR 28 and Spo, 94%. The diagnosis of suspected spinal cord injury was made and methylprednisolone loading dose of 30mg/kg was initiated. Left arm splinted. Report was called to the local hospital Emergency Department (ED), and the patient was placed on a backboard and transported with no difficulties. On arrival to the hospital, the emergency medicine healthcare provider quickly assessed the patient and determined he was hemodynamically stable and he should be emergently transferred to the regional spinal cord injury center for specialized medical care. Learning Objectives: 1. Utilizes the patient history and assessment data to plan, prioritize, individualize and provide care for a person with a spinal cord injury that develops neurogenic shock (SYNTHESIS). 2. Anticipates diagnostic orders and therapies, including medications, for the patient with neurogenic shock (COMPREHENSION). 3. Discusses the possible consequences of unrecognized neurogenic shock (COMPREHENSION). 4. Phoritizes the implementation and approach to the nursing care of a patient in neurogenic shock (ANALYSIS). 5. Evaluates the patient’s response to interventions and modifies the nursing care as appropriate for the patient in neurogenic shock (EVALUATION) Healthcare Provider’s Orders/Questlong Continuous ECG and Spo, monitoring Vital signs and neurological assessment every 1 hour Oxygen 2LPM via nasal canula: titrate to keep Spo, greater than 95% Incentive spirometer every hour while awake Cough and deep breathe every hour while awake NPO CBC with differential, Electrolytes, BUN Creatinine, Glucose, ABG on arrival and every AM CT scan, of the spine, no contrast X-ray of left arm and shoulder Chest x-ray on admission and every other AM N 0.9% NS at 80ml/hour Methylprednisolone 5.4mg/kg continuous I infusion for 24 hours Strict bedrest; maintain spinal precautions, logroll only Rigid cervical collar Antiembolic stockings and sequential compression device for deep vein thrombosis (DVT) prophylaxis Famotidine 20mg I twice daily Morphine sulfate 1-2mg I every 1 hour pm for pain Notify healthcare provider for: HR greater than 140 or less than 60 Systolic BP less than 90 or greater than 180 Temp greater than 38°C SpO2 less than 92% Urine output less than 30ml/hour x 2 hours Any neurologic changes 5 1. Discuss all pertinent assessment findings of this patient with spinal cord injury and link them to the bodily changes from the accident, which resulted in the changes in his condition. 2. Discuss the anticipated lab and diagnostic tests that this patient would undergo when he arrived to the Emergency Room. 3. What are 4 acute goals of nursing management for the patient with neurogenic shock when in the ICU? 4. Identify 1 primary nursing diagnoses for this patient with spinal cord injury, focused on the first 24 hours in the ICU. Use the correct NANDA format, complete with a “related to 5. This patient goes on to experience sustained bilateral lower extremity paralysis and is wheelchair bound, at 1 month after the “fall off the roof” accident. He is discharged to home after a stay in a rehab unit. List 1 priority nursing diagnoses for this patient that you would expect to see, as a home health nurse. Use the correct NANDA format, complete with a “related to 6. What are the complications associated with neurogenic shock? Medications: 7. Explain the intended effects ( desired actions) of methylprednisolone via continuous IV infusion, as stated in the MD’s orders. 8. Explain the intended effects ( desired actions) of famotidine via IV route BID, as stated in the MD’s orders. 9. Explain the intended effects desired actions) of morphine sulfate 1-2 mg, every 1 hr prn, via IV push, as stated in the MD’s orders. 10. List all the nursing interventions to keep the spine stabilized – as noted in this case.
(Visited 4 times, 1 visits today)