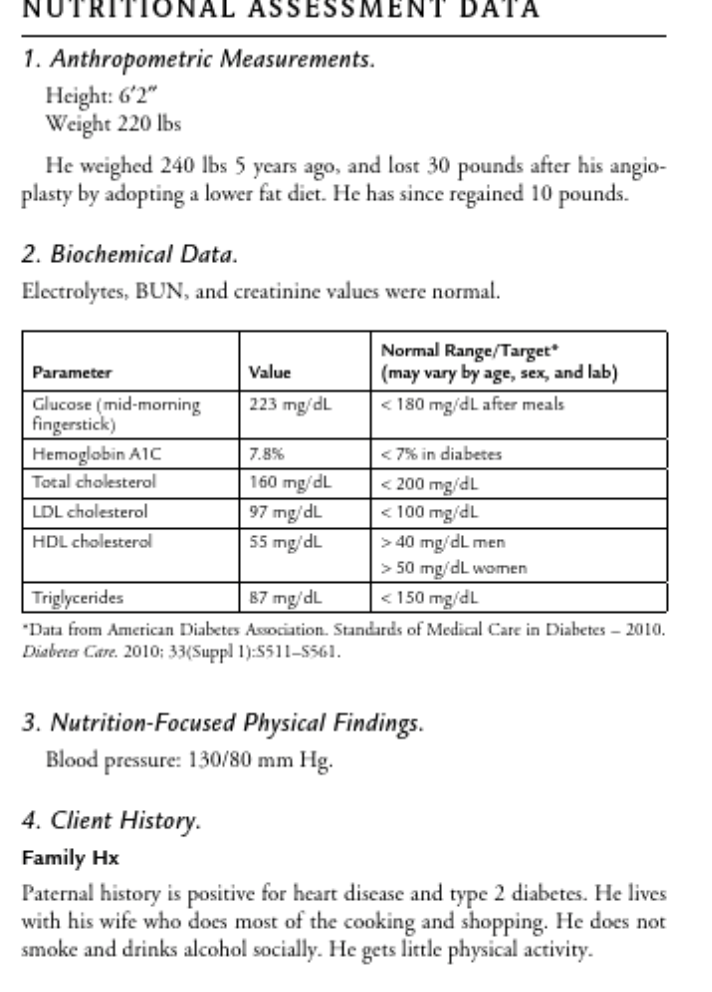
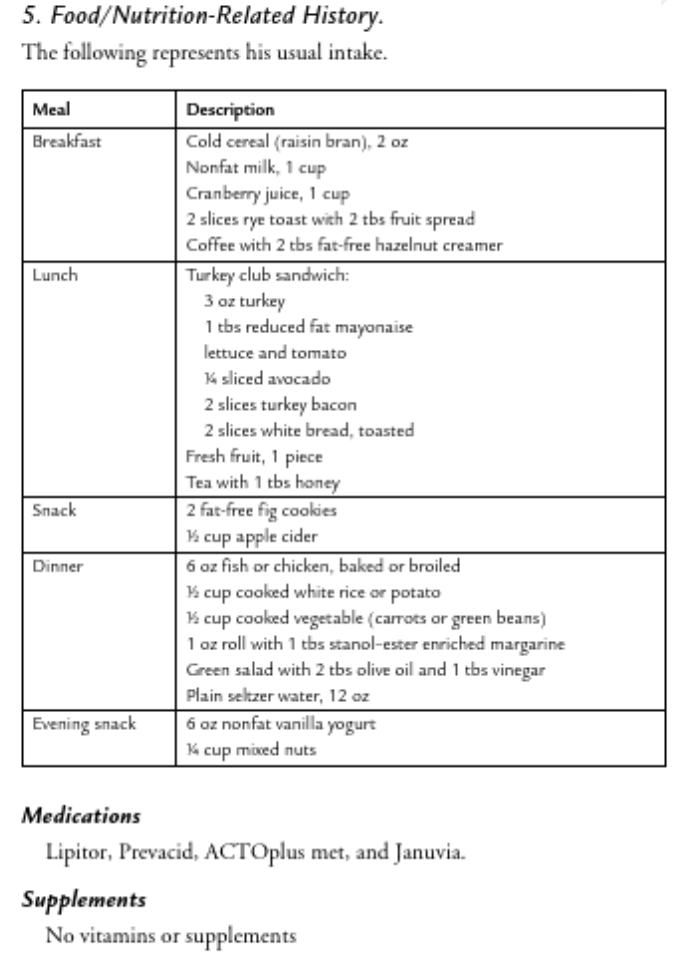
The client is a 73-year-old man diagnosed one year ago with type2 diabetes mellitus. He has a history of coronary heart disease s/pangioplasty 5 years prior, hypertension, retinopathy, and left footneuropathy. He makes every attempt to follow a healthy diet, andhas been avoiding table sugar for the past year on his physician’sadvice. He comes to see the registered dietitian due to apersistently elevated hemoglobin A1c.
1. Describe the management of bloodglucose through intensive insulin therapy including self-monitoringof blood glucose (SMBG) and multiple daily injections of insulin(MDI). What are the advantages and disadvantages of thisapproach?
2. What is considered an optimal HbA1clevel for a patient with diabetes? What are the goals forpreprandial and peak postprandial blood glucose levels?
3. What are signs and symptoms ofhypoglycemia? How would you recommend that he treats hishypoglycemia? Give specific suggestions.
4. Write a PES statement for thispatient upon presentation. What are your goals for this patient?How would you monitor the outcome (results) of his dietarytreatment? List indicators and criteria that you would monitor,addressing allcomponents of Nutrition Assessment (A,B,C,D,H).