top picture is assignment, rest is supplemental info and HEDmeans Human Equivalent Dosey


Transcribed Image Text from this Question
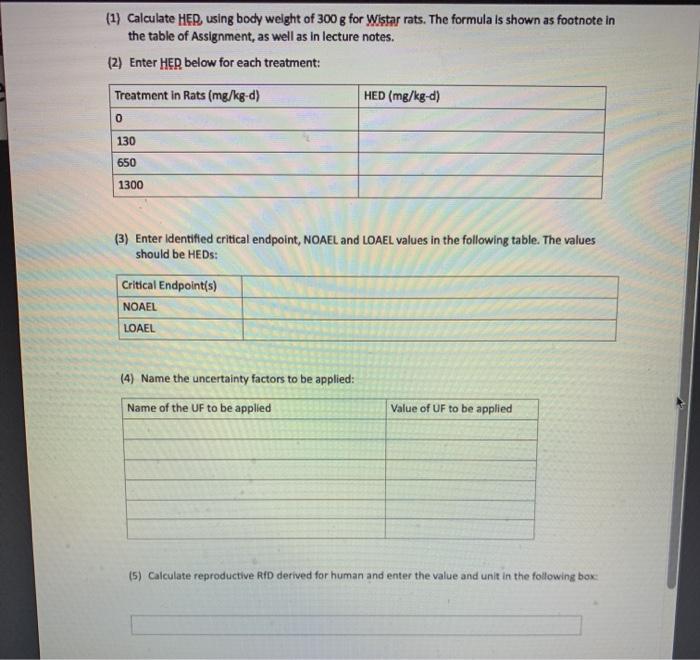
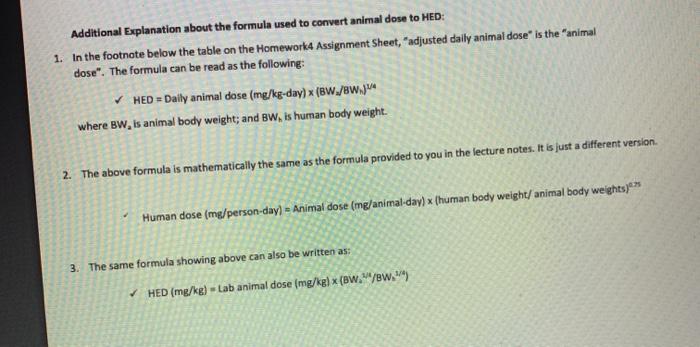
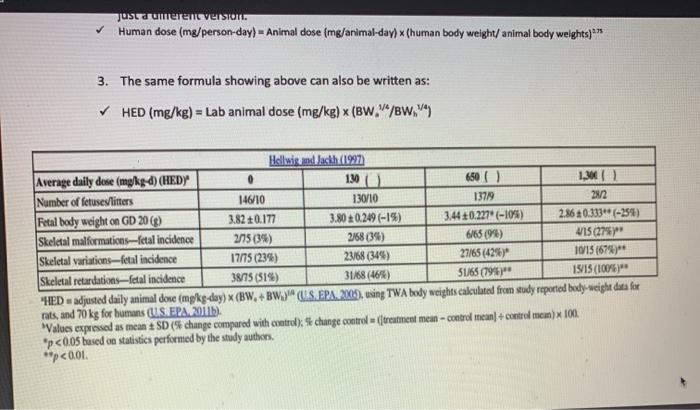
(1) Calculate HER, using body weight of 300 g for Wistar rats. The formula is shown as footnote in the table of Assignment, as well as in lecture notes. (2) Enter HER below for each treatment: Treatment in Rats (mg/kg-d) HED (mg/kg-d) 0 130 650 1300 (3) Enter identified critical endpoint, NOAEL and LOAEL values in the following table. The values should be HEDs: Critical Endpoint(s) NOAEL LOAEL (4) Name the uncertainty factors to be applied: Name of the UF to be applied Value of UF to be applied (5) Calculate reproductive RfD derived for human and enter the value and unit in the following box Additional Explanation about the formula used to convert animal dose to HED: 1. In the footnote below the table on the Homework Assignment Sheet, adjusted daily animal dose” is the “animal dose”. The formula can be read as the following: HED = Daily animal dose (mg/kg-day) x (BW./8w.jm where BW, is animal body weight; and BW, is human body weight 2. The above formula is mathematically the same as the formula provided to you in the lecture notes. It is just a different version. Human dose (mg/person-day) – Animal dose (mg/animal-day) x (human body weight/animal body weights)*** 3. The same formula showing above can also be written as: HED (mg/kg) – Lab animal dose (mg/kg) x (BW./ew.” Background information: Rats body weight is about 300 g on average during gestation. Rat gestation is about 21 days. Human gestation is about 280 days. Human body weight, use 65 kg. Study method: Pregnant rats, 10 rats per treatment group, were treated by gavage from day 6 to day 15 of gestation. On Day 20 of gestation, fetuses were examined for body weight and skeletal abnormalities. See results in table below. Classroom discussion: In the described study, is the length of exposure during pregnancy, i.e. 10 days in rats, a short-term or a long-term exposure? Use 3 for short term to long term extrapolation. Additional Explanation about the formula used to convert animal dose to HED: 1. In the footnote below the table on the Homework4 Assignment Sheet, “adjusted daily animal dose” is the “animal dose”. The formula can be read as the following: ✓ HED = Dally animal dose (mg/kg-day) x (BW./BW.)” where BW, is animal body weight; and BW, is human body weight. 2. The above formula is mathematically the same as the formula provided to you in the lecture notes. It is just a different version. Human dose (mg/person-day) – Animal dose (mg/animal-day) x (human body weight/animal body weights) ** 3. The same formula showing above can also be written as: ✓ HED (mg/kg) – Lab animal dose (mg/kg) x (BW.M/BW.44) Just a umerene version. Human dose (mg/person-day) – Animal dose (mg/animal-day) x (human body weight/animal body welghts)** 3. The same formula showing above can also be written as: HED (mg/kg) = Lab animal dose (mg/kg) x (BW.M/BW.V) Hellwig and Jackh (1997 Average daily dose (mg/kg-d) (HEDY 650 () 1,36 Number of fetuses/litters 146/10 130/10 13719 23/2 Fetal body weight on GD 20 (9) 3.82 +0.177 3.80 +0.249 (-19) 3.44 0.227″ (-10%) 2.86 +0.333** (-25%) Skeletal malformations–fetal incidence 2015 (39) 2868 (39) 6/65 (98) 4/15 27% Skeletal variations-fetal incidence 17/75 (23%) 23/68 (34) 27765 (428) 10/15 (67%)** Skeletal retardations-fetal incidence 38/75(51%) 31/68 (46) 51/65 (798)** 15/15 (100%)” “HED – adjusted daily animal dose (mg/kg-day) x (BW.BW.MUS. EPA. 2009, using TWA body weights calculated from study reported body weight data fox rats, and 70 kg for humans (LLS EPA 2011). “Values expressed as mean + SD (5 change compared with control chunge control treatment mean-control mean] + control mean) 100 *p<0.05 based on statistics performed by the study authors **p<0.01.
(Visited 2 times, 1 visits today)



